The Power of Ozone: How It Kills Bacteria and Pathogens Naturally
Ozone can be used in many industries for purification and disinfection. The most significant benefit of ozone is its pure characteristic. It is eco-friendly and sustainable as it is produced by a generator onsite.
Ozone, a powerful molecule with three oxygen atoms (O3), is gaining recognition as an effective, eco-friendly disinfectant. Known for its ability to break down bacteria, viruses, and other harmful pathogens, ozone works by a process that is both natural and highly efficient. In this article, we’ll explore how ozone molecules neutralize bacteria and pathogens and why this makes it a valuable tool in disinfection.
1. What Makes Ozone Effective?
Ozone is an unstable molecule due to its extra oxygen atom. When ozone comes into contact with bacteria, viruses, or other organic contaminants, it readily releases one oxygen atom, turning back into oxygen (O2). This free oxygen atom is highly reactive, seeking out and attaching to molecules in the bacteria or virus, causing a rapid breakdown of their structure.
Ozone, a powerful molecule with three oxygen atoms (O3), is gaining recognition as an effective, eco-friendly disinfectant. Known for its ability to break down bacteria, viruses, and other harmful pathogens, ozone works by a process that is both natural and highly efficient. In this article, we’ll explore how ozone molecules neutralize bacteria and pathogens and why this makes it a valuable tool in disinfection.
1. What Makes Ozone Effective?
Ozone is an unstable molecule due to its extra oxygen atom. When ozone comes into contact with bacteria, viruses, or other organic contaminants, it readily releases one oxygen atom, turning back into oxygen (O2). This free oxygen atom is highly reactive, seeking out and attaching to molecules in the bacteria or virus, causing a rapid breakdown of their structure.
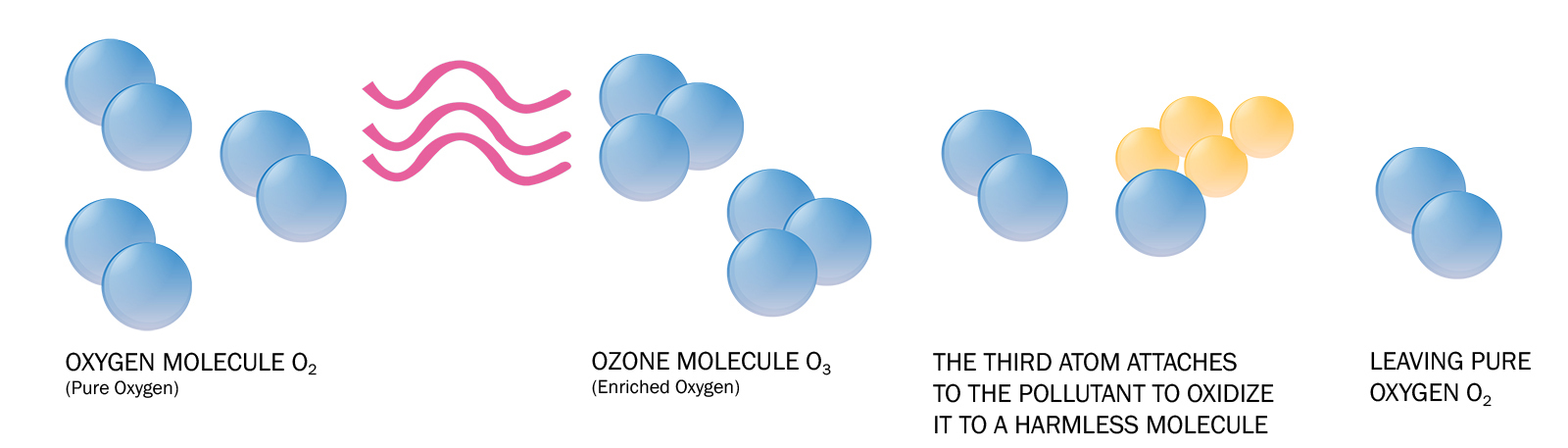
2. How Ozone Attacks Bacteria and Pathogens
Ozone destroys bacteria and pathogens through oxidation. Here’s a closer look at the steps involved:
Ozone destroys bacteria and pathogens through oxidation. Here’s a closer look at the steps involved:
- Membrane Disruption: Ozone molecules attack the cell walls of bacteria and the outer coating of viruses. The oxidative action disrupts the cell membrane, leading to cell lysis (bursting), which kills the pathogen almost instantly.
- Intracellular Damage: Once the cell wall is compromised, ozone penetrates the cell, damaging essential cellular components like proteins, enzymes, and DNA. This prevents the bacteria or virus from repairing itself, further ensuring that it cannot replicate or cause harm.
- Immediate Action: The process is quick and effective, with ozone killing many types of pathogens upon contact. The released oxygen atoms actively break down contaminants without leaving behind any harmful residues.
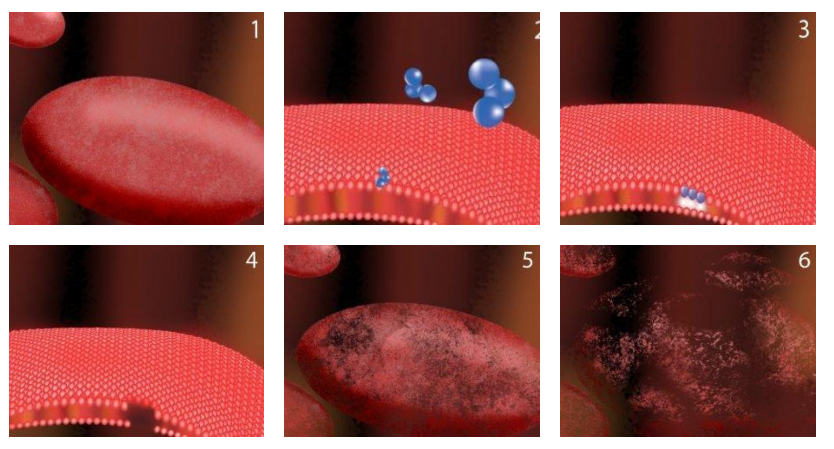
3. Types of Pathogens Ozone can Neutralize
Ozone has shown effectiveness against a wide range of harmful pathogens, including:
Ozone has shown effectiveness against a wide range of harmful pathogens, including:
- Bacteria: E. coli, Salmonella, and Staphylococcus are just a few examples of bacteria that ozone can kill. Studies show that ozone can eliminate up to 99.99% of bacteria within minutes.
- Viruses: Ozone is effective against viruses such as influenza and certain types of coronaviruses by targeting the lipid and protein structures in their outer layers.
- Fungi and Mold: Ozone can also kill mold spores and fungi, making it ideal for disinfecting areas prone to mold growth.
- And even more - Check this link: https://ozonesolutions.com/blog/ozone-effects-on-pathogens/
4. Benefits of Using Ozone in Disinfection
Ozone stands out from other disinfectants for several reasons:
- Environmentally Friendly: Unlike traditional disinfectants that leave behind chemical residues, ozone naturally decomposes back into oxygen.
- Broad-Spectrum Effectiveness: Ozone effectively targets a wide range of microbes, including those that might be resistant to other disinfectants.
- Non-Toxic Residue: After doing its job, ozone simply breaks down, leaving no toxic or harmful residues in the environment.
5. Practical Applications of Ozone Disinfection
Given its efficiency, ozone has numerous applications:
Given its efficiency, ozone has numerous applications:
- Healthcare Facilities: Ozone is used to disinfect surfaces, equipment, and air in hospitals to maintain a sterile environment.
- Food Safety: Ozone is commonly used to sanitize fruits, vegetables, and surfaces in food processing industries.
- Water Treatment: Ozone is applied in purifying drinking water and treating wastewater, effectively reducing harmful microbes without the need for harsh chemicals.
- Domestic and Personal use: Everyone can use ozone for washing and cleaning purposes, sanitizing hands, even oral care every day…
6. Safety Considerations When Using Ozone
While ozone is highly effective, it’s essential to use it in controlled amounts and with proper ventilation. While high ozone concentration can be harmful if inhaled (exposure at 50 ppm for 60 minutes will probably be fatal to humans), Ozone water, or aqueous ozone, is regarded as safe for human skin since a concentration of just 0.3 ppm is sufficient to kill bacteria.. In controlled disinfection settings, ozone water is safe and decomposes quickly, no exposure risk.
Conclusion
Ozone disinfection is a powerful method for neutralizing bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens through oxidation. Its rapid action and natural decomposition make it a safe, eco-friendly alternative to traditional disinfectants. As the world seeks more sustainable disinfection solutions, ozone stands out as a compelling option for safer and more effective pathogen control.
Learn more about Ozone Water Technology in our other articles.
Follow us on LinkedIn
While ozone is highly effective, it’s essential to use it in controlled amounts and with proper ventilation. While high ozone concentration can be harmful if inhaled (exposure at 50 ppm for 60 minutes will probably be fatal to humans), Ozone water, or aqueous ozone, is regarded as safe for human skin since a concentration of just 0.3 ppm is sufficient to kill bacteria.. In controlled disinfection settings, ozone water is safe and decomposes quickly, no exposure risk.
Conclusion
Ozone disinfection is a powerful method for neutralizing bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens through oxidation. Its rapid action and natural decomposition make it a safe, eco-friendly alternative to traditional disinfectants. As the world seeks more sustainable disinfection solutions, ozone stands out as a compelling option for safer and more effective pathogen control.
Learn more about Ozone Water Technology in our other articles.
Follow us on LinkedIn
